Sarcopenia meaning, muscle loss with age and it’s treatment
What is Sarcopenia?
This condition can be influenced by various factors, including hormonal changes, decreased physical activity, inadequate protein intake, and other underlying health conditions. To combat sarcopenia or slow its progression, regular physical activity, especially resistance or strength training, and a balanced diet rich in protein and essential nutrients are recommended.
Early detection and intervention are essential in managing sarcopenia effectively. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms associated with sarcopenia, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and personalized management strategies.
Risk Factors for Sarcopenia
Aging:
Sarcopenia is primarily associated with the natural aging process. As people get older, they tend to experience a gradual loss of muscle mass and strength.
Sedentary lifestyle:
Lack of regular physical activity, especially exercises that involve resistance or strength training, can contribute to muscle loss and increase the risk of sarcopenia.
Poor nutrition:
Inadequate protein intake and a diet lacking essential nutrients can impair muscle maintenance and repair, making individuals more susceptible to sarcopenia.
Hormonal changes:
Changes in hormone levels, particularly a decline in testosterone and growth hormone in men and estrogen in women, can contribute to muscle loss.
Chronic diseases:
Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, chronic kidney disease, rheumatoid arthritis, and cancer, can increase the risk of sarcopenia.
Immobility or disability:
Conditions that restrict mobility or limit physical activity, such as fractures, joint problems, or neurological disorders, can accelerate muscle loss.
Inflammation:
Chronic inflammation in the body may play a role in the development of sarcopenia.
Genetics:

Family history and genetic factors can influence an individual’s susceptibility to sarcopenia.
Medications:
Some medications, such as corticosteroids and certain antidepressants, may contribute to muscle loss.
It’s important to note that while aging is a primary risk factor, not everyone will develop sarcopenia as they age. Engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy diet, and adopting a proactive approach to health and fitness can help reduce the risk and mitigate the effects of sarcopenia. If you are concerned about sarcopenia or its risk factors, discussing it with a healthcare professional can provide valuable insights and personalized recommendations.
Problems Caused by Sarcopenia
- Muscle Mass Reduction:
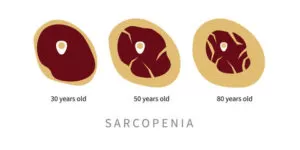
Sarcopenia leads to a decrease in the size and quantity of muscle fibers in the body. As people age, muscle protein synthesis declines, and there is a higher rate of muscle protein breakdown. This imbalance results in a net loss of muscle tissue over time.
- Muscle Weakness:
With the loss of muscle mass, there is a corresponding decline in muscle strength. Individuals with sarcopenia may find it increasingly challenging to perform everyday activities that require physical effort, such as climbing stairs, lifting objects, or getting up from a chair.
- Impaired Physical Function:
Sarcopenia can significantly impact an individual’s physical function and mobility. Reduced muscle strength and mass can lead to decreased balance, stability, and coordination, making people more susceptible to falls and injuries.
- Metabolic Changes:
Sarcopenia can influence the body’s metabolism. With reduced muscle mass, the body’s ability to burn calories may decrease, potentially leading to weight gain or difficulty in maintaining a healthy weight.
- Increased Fat Accumulation
As muscle mass decreases, there may be an increase in fat accumulation, particularly in the abdominal region. This change in body composition can further contribute to metabolic disturbances.
- Decreased Bone Density:
Muscle and bone health are interconnected. Reduced muscle mass can lead to decreased mechanical stress on bones, potentially contributing to decreased bone density and an increased risk of osteoporosis.
- Loss of Independence:
Severe sarcopenia can impact an individual’s ability to perform daily tasks independently, leadings to a loss of autonomy and reduced quality of life.
- Frailty:
Sarcopenia is often associated with frailty, a state of increased vulnerability to stressors and a higher risk of adverse health outcomes.
It’s essential to address sarcopenia early through lifestyle interventions. Sedentary Lifestyle increases the speed of muscle loss which causes sarcopenia in early age or in the perimenopausal phase in women’s but in men’s it happens in 60’s or later on.
Treatment for sarcopenia
Age-related declines in muscle size, strength, and functionality are referred to as sarcopenia. Older persons who have it are more likely to experience diminished mobility, a higher chance of falling, and a general decline in quality of life. While there isn’t a single, effective treatment for sarcopenia, managing the illness may benefit from a mix of dietary adjustments, physical activity, and, in some circumstances, medical therapies. The following strategies can be taken into account:
1. Exercise and physical activity:
Fighting sarcopenia requires regular physical activity, especially resistance training (strength training). Exercises for strength training, including lifting weights, utilizing resistance bands, or bodyweight exercises, can aid in gaining and maintaining muscular mass. Major muscle groups should be the focus of an exercise program that gradually increases the intensity over time. Before beginning any workout plan, especially for older folks, it’s crucial to speak with a healthcare practitioner or certified fitness trainer.
2. Intake of Protein: For the preservation and regeneration of muscles, an adequate intake of protein is necessary. The building blocks for the development of muscles are provided by protein. Lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy products, legumes, and nuts are some examples of foods high in protein that can help maintain healthy muscles.
3. Nutrition: For overall health and muscle function, a balanced diet with a variety of nutrients is crucial, in addition to protein. Muscle health can be supported by consuming enough vitamins and minerals, such as calcium, magnesium, and vitamin D.
4.Caloric Intake: Maintaining a healthy weight is essential since rapid weight loss might accelerate the loss of muscle. On the other hand, reduced muscular function can also be a result of too much body fat. Determining an optimum calorie intake to assist muscle preservation while managing weight might be made easier by consulting a healthcare professional or nutritionist.
5. Hormone Replacement Therapy: Hormonal abnormalities, such as low testosterone in men, can occasionally cause sarcopenia. A healthcare professional-supervised hormone replacement therapy may be taken into account as part of the treatment strategy.
6.Pharmaceuticals and dietary supplements: A number of pharmaceuticals and dietary supplements are being researched for their possible management of sarcopenia. These include omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin D supplements, and drugs that could enhance muscle function. Their efficacy is still being studied, so talking to a healthcare professional before using them is advised.
7. Fall Prevention: Due to decreased strength and balance, sarcopenia might increase the risk of falling. It’s crucial to take steps to prevent falls, such as enhancing home security, donning the proper footwear, and performing activities that improve balance, to prevent accidents.
8. Medical Evaluation: If you or a loved one is losing a lot of muscle mass, it’s crucial to speak with a medical expert. They are able to determine the root reasons, carry out the required testing, and offer specific management advice for sarcopenia.
These measures can help slow down the progression of sarcopenia and improve overall physical function and well-being.
If you suspect you or someone you know may have sarcopenia, consulting a healthcare professional is crucial for proper evaluation and personalized management. A complete strategy that incorporates exercise, nutrition, and medical advice is frequently the best course of action. Keep in mind that the success of treatment may differ based on certain conditions. Before making any big modifications to your workout or treatment routine, it is always advisable to speak with a healthcare professional.


